The Earth, our bright blue marble, is in a state of flux. Temperatures are rising, the ice caps are melting, and weather patterns are becoming more unpredictable. These aren’t just blips on the radar; they’re the telltale signs of global warming, a phenomenon that threatens the very fabric of our planet and our way of living. In This blog we will discuss about Characteristics Global Warming
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Characteristics Global Warming
What is Global Warming?
Global warming is the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature caused by human activity, primarily the release of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, gradually warming the earth.
Factors Contributing to Global Warming
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels for energy and deforestation, emit large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Industrialization: The surge in industrial activity has greatly increased the concentration of pollutants, which contributes to the greenhouse effect.
- Deforestation: The destruction of forests limits the number of trees that absorb CO2, exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
- Waste Management: Improper waste disposal and landfill procedures emit methane, a strong greenhouse gas, into the environment.
Impacts of Global Warming
1.The Unequivocal Rise in Temperature:
The most defining characteristic of global warming is the unprecedented increase in Earth’s average temperature. Since the pre-industrial era, the globe has warmed by around 1 degree Celsius, an apparently insignificant figure that masks the enormous implications. The accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, is the primary driver of this warming trend. These gases operate as a blanket, trapping heat from the sun and causing the earth to roast.
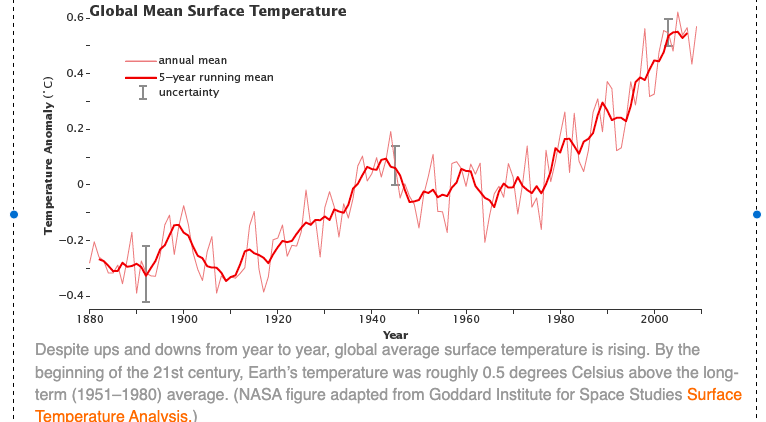
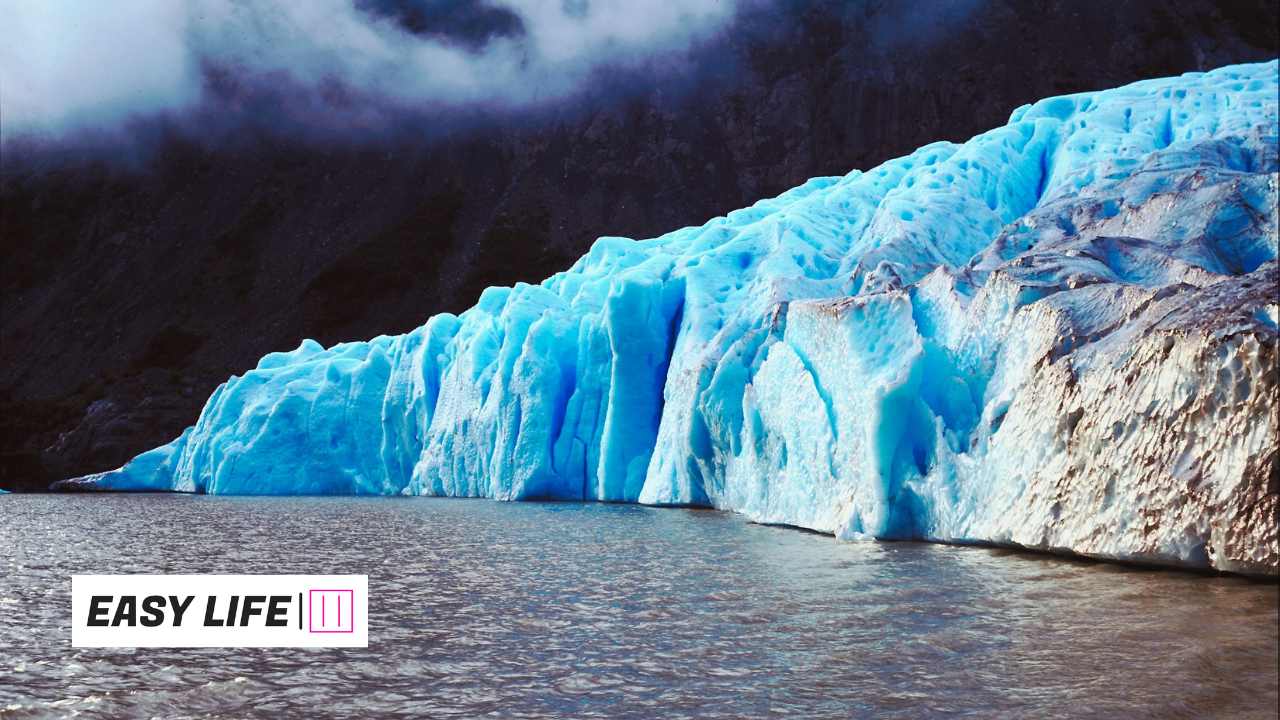
2.Melting Ice and Rising Seas:
One of the most noticeable effects of global warming is the melting of glaciers and ice caps. As temperatures rise, these massive reservoirs of frozen water melt, leading to rising sea levels. This poses a serious threat to coastal towns, low-lying islands, and fragile ecosystems all around the world.

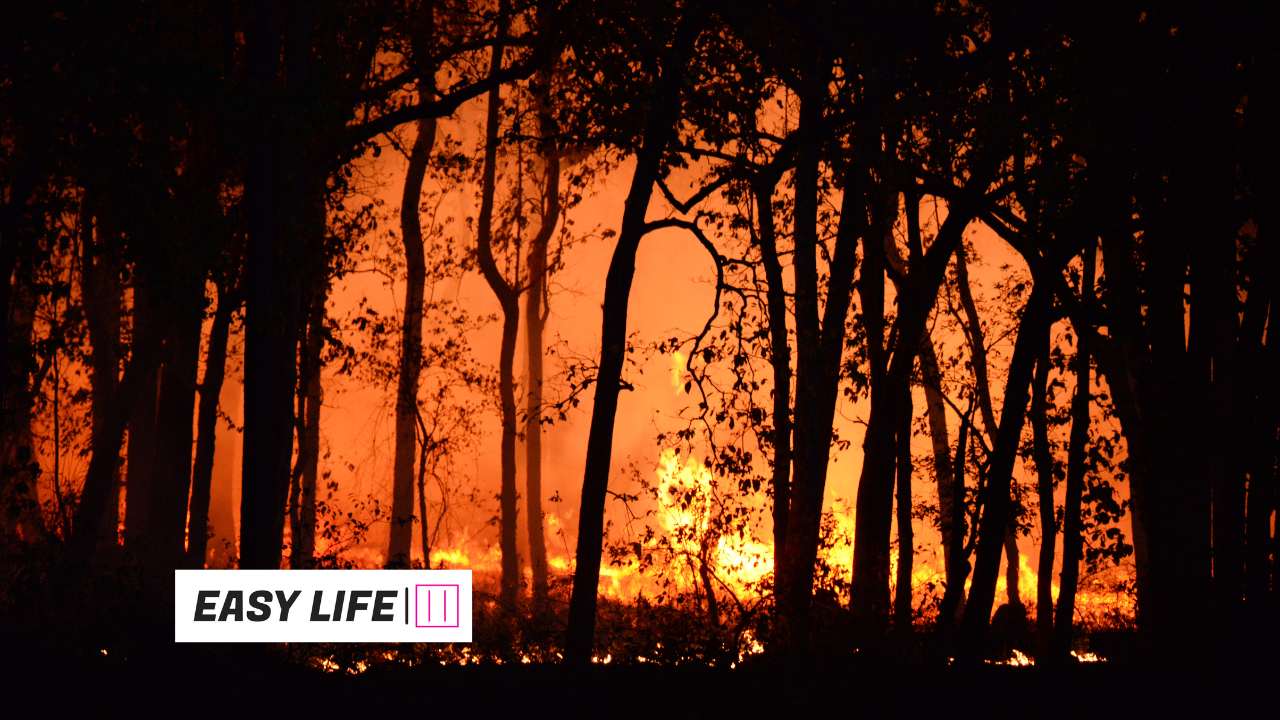
3.Weather Gone Wild:
Global warming is also upsetting the delicate balance of the Earth’s climate system, resulting in increasingly severe and unpredictable weather occurrences. Heatwaves, droughts, floods, and wildfires are becoming more common and severe, causing widespread destruction and relocation.

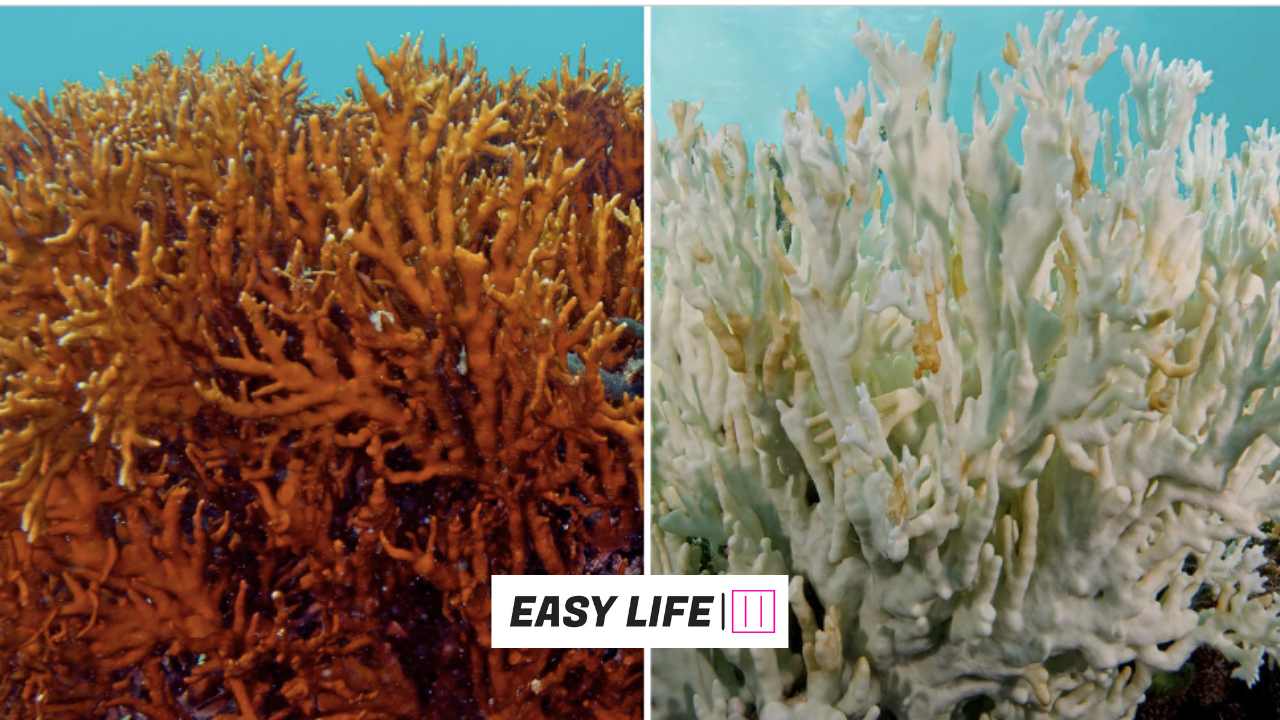
The Domino Effect on Ecosystems:
Global warming has far-reaching consequences for the planet’s ecosystems, in addition to physical changes. Rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns are disturbing habitats, putting species on the verge of extinction, and affecting food chains. Coral reefs, which are critical for marine biodiversity, are bleaching and dying owing to rising ocean temperatures.

A Global Challenge, a Shared Responsibility:
Global warming is not a singular problem; it is a global concern that necessitates a worldwide response. Every individual, community, and nation can help mitigate the effects and develop a more sustainable future. Understanding the characteristics of global warming and its far-reaching implications allows us to take educated action and work together to protect our planet for future generations.
Here are a few ways you may help battle global warming:

- Reduce your carbon footprint: This includes using energy-efficient appliances, opting for public transportation or cycling, and reducing your consumption of meat and dairy products.
- Support renewable energy: Advocate for policies that promote renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal power.
- Conserve water: Every drop counts! Fix leaky faucets, take shorter showers, and water your lawn more efficiently.
- Spread awareness: Talk to your friends and family about global warming and encourage them to take action.
- Support organizations working on climate change solutions: Donate your time or resources to organizations working to address climate change.
FAQs on Global Warming
Q1: How does global warming occur?
A1: Global warming is primarily caused by growing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere. Human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation emit these gases, trapping heat and causing the world to overheat.
Q2: What are the main greenhouse gases responsible for global warming?
A2: The main greenhouse gases responsible for global warming include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to the warming of the planet.
Q3: How does deforestation contribute to global warming?
A3: Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases are among the most important greenhouse gases contributing to global warming. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which contributes to global warming.
Q4: What are the consequences of rising global temperatures?
A4: Rising global temperatures cause a variety of effects, including more frequent and intense heatwaves, droughts, melting ice caps and glaciers, rising sea levels, and a rise in the frequency of extreme weather events.
Q5: How does global warming affect marine life?
A5: Global warming adds to ocean acidification, which harms marine life. The increased absorption of carbon dioxide by seas causes acidification, endangering coral reefs and marine ecosystems.
Conclusion:characteristics of global warming
To summarise, understanding the characteristics of global warming is critical for addressing this environmental issue. Understanding the elements that contribute to global warming and its far-reaching consequences allows us to work together to develop long-term solutions. The FAQ section answers frequently asked questions, helping readers understand the complexities of global warming. As stewards of the Earth, it is our responsibility to take proactive steps to reduce global warming and secure a sustainable future for future generations.
Some External Resources
- Scientific Reports and Studies:
- Educational Websites:
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs):
- News and Media Outlets:
- Government Resources:
- Books:
- Documentaries and Films:
- Online Platforms:






